A healthy diet is one that helps to maintain or improve overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients, micronutrients, and adequate calories.
The requirements for a healthy diet can be met from a variety of plant-based and animal-based foods, although a non-animal source of vitamin B12 is needed for those following a vegan diet. Various nutrition guides are published by medical and governmental institutions to educate the public on what they should be eating to promote health. Nutrition facts labels are also present on most packaged foods and can be used to make informed food choices.
The Australian Dietary Guidelines (ADG) are designed to promote health and reduce the risk of diet-related diseases. They are based on the best available scientific evidence and provide recommendations for healthy eating for people aged two years and over. The Guidelines are updated every five years, with the most recent edition released in 2013.
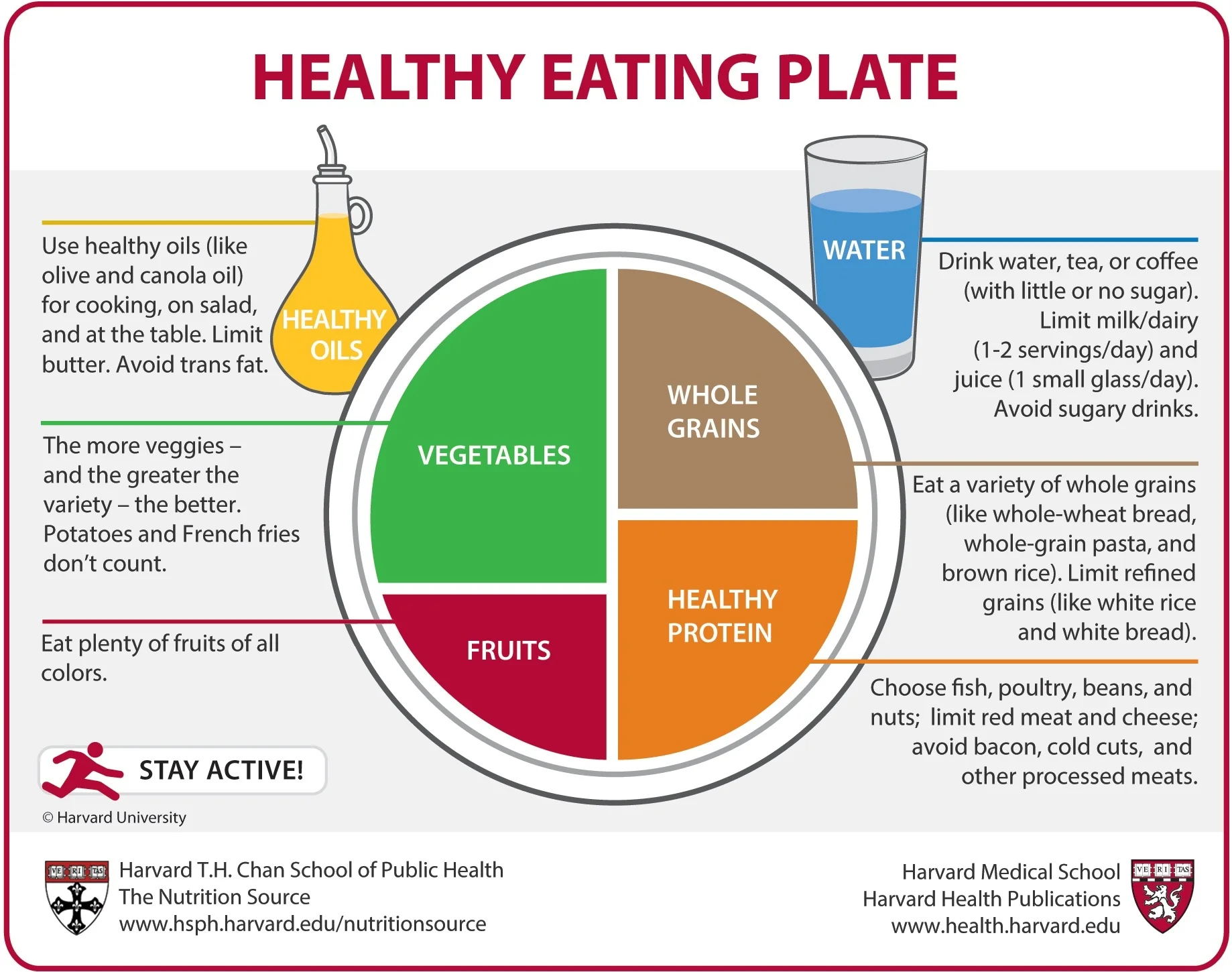
The ADG suggest that adults eat a variety of nutritious foods from the five food groups every day. These food groups are:
• Breads, cereals, rice, pasta, noodles
• Vegetables, legumes, beans
• Fruit
• Milk, yoghurt, cheese
• Lean meat, fish, poultry, eggs, nuts, seeds
In addition, the Guidelines recommend that adults:
• limit their intake of foods high in saturated fat, added sugar, added salt and alcohol
• eat plenty of water
• be physically active.
The ADG are relevant to all Australians, including those from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds. They provide a flexible framework to enable people to make choices about the foods they eat, within the context of their own food preferences, culture and traditions.
The Guidelines are not a diet plan or a list of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ foods. Rather, they provide an overall approach to healthy eating.
The key messages from the Guidelines are:
• enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from the five food groups every day
• limit intake of foods and drinks high in saturated fat, added sugar, added salt and alcohol
• be physically active every day.
The Australian Dietary Guidelines (2013) are available from the Department of Health website.
The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating is a food selection guide which visually represents the proportion of the five food groups recommended for consumption each day.
The Guide shows that adults should eat:
• plenty of vegetables, legumes and fruits
• mostly wholegrain cereals
• lean meat and poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, nuts and seeds
• milk, yoghurt, cheese and/or their alternatives, mostly reduced fat
• only small amounts of foods and drinks high in saturated fat, added sugar, added salt and alcohol.
The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating is available from the Department of Health website.
The Healthy Eating Pyramid is a visual guide to the types and proportion of foods that we should eat every day for good health.
The Pyramid shows that the foundation of a good diet is daily exercise and eating mostly foods from the base of the Pyramid. These include:
• vegetables and legumes
• fruits
• wholegrains
• lean meat, fish, poultry, eggs, tofu, nuts and seeds
• milk, yoghurt, cheese and/or their alternatives, mostly reduced fat.
The Healthy Eating Pyramid is available from the Department of Health website.
The Healthy Weight Pyramid is a visual guide to the types and proportion of foods that we should eat every day to maintain a healthy weight.
The Healthy Weight Pyramid is available from the Department of Health website.
The Physical Activity Pyramid is a visual guide to the types and amount of physical activity that we should do every day for good health.
The Pyramid shows that the foundation of a good physical activity regime is moderate intensity aerobic activity, such as walking, and doing muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
The Physical Activity Pyramid is available from the Department of Health website.
The Australian Dietary Guidelines (ADG) provide advice on the types and amounts of foods, food groups and dietary patterns that aim to promote health and wellbeing, reduce the risk of diet-related conditions and chronic diseases, and support healthy growth and development in children and adolescents.
The Guidelines are based on the best